Darkover
Archangel
- Jul 29, 2021
- 5,649
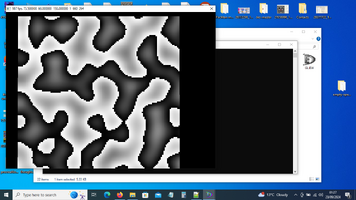
2D Perlin noise is a gradient noise function commonly used in computer graphics and procedural generation. It generates a smooth, continuous, and random-looking pattern in two dimensions.
Overall, 2D Perlin noise is widely used in game development and other graphical applications for generating realistic textures and natural patterns
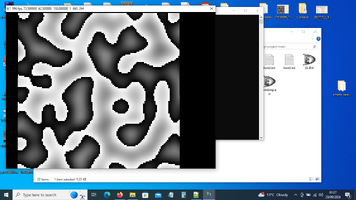
Overall, 2D Perlin noise is widely used in game development and other graphical applications for generating realistic textures and natural patterns
C:
-- Original permutation table
sequence base_permutation
base_permutation= {151, 160, 137, 91, 90, 15, 131, 13, 201, 95, 96, 53, 194, 233, 7, 225,
140, 36, 103, 30, 69, 142, 8, 99, 37, 240, 21, 10, 23, 190, 6, 148,
247, 120, 234, 75, 0, 26, 197, 62, 94, 252, 219, 203, 117, 35, 11, 32,
57, 177, 33, 88, 237, 149, 56, 87, 174, 20, 125, 136, 171, 168, 68, 175,
74, 165, 71, 134, 139, 48, 27, 166, 77, 146, 158, 231, 83, 111, 229, 122,
60, 211, 133, 230, 220, 105, 92, 41, 55, 46, 245, 40, 244, 102, 143, 54,
65, 25, 63, 161, 1, 216, 80, 73, 209, 76, 132, 187, 208, 89, 18, 169,
200, 196, 135, 130, 116, 188, 159, 86, 164, 100, 109, 198, 173, 186, 3, 64,
52, 217, 226, 250, 124, 123, 5, 202, 38, 147, 118, 126, 255, 82, 85, 212,
207, 206, 59, 227, 47, 16, 58, 17, 182, 189, 28, 42, 223, 183, 170, 213,
119, 248, 152, 2, 44, 154, 163, 70, 221, 153, 101, 155, 167, 43, 172, 9,
129, 22, 39, 253, 19, 98, 108, 110, 79, 113, 224, 232, 178, 185, 112, 104,
218, 246, 97, 228, 251, 34, 242, 193, 238, 210, 144, 12, 191, 179, 162, 241,
81, 51, 145, 235, 249, 14, 239, 107, 49, 192, 214, 31, 181, 199, 106, 157,
184, 84, 204, 176, 115, 121, 50, 45, 127, 4, 150, 254, 138, 236, 205, 93,
222, 114, 67, 29, 24, 72, 243, 141, 128, 195, 78, 66, 215, 61, 156, 180}
-- Function to shuffle the permutation table
function shuffle(sequence perm)
integer n,j,temp
n= length(perm)
for i = n to 2 by -1 do
j = rand(i)
-- Swap elements
temp = perm[i]
perm[i] = perm[j]
perm[j] = temp
end for
return perm
end function
-- Seed the random number generator with the current time
set_rand(get_tick_count())
-- Create a shuffled permutation table
sequence permutation
permutation = shuffle(base_permutation)
-- Double the permutation table to avoid overflow when indexing
permutation &= permutation
-- Helper function for modulo operation in Euphoria 3.1
function mod(integer a, integer b)
return a - b * floor(a / b) +1
end function
-- Function to generate gradient vectors based on the permutation table
function gradient(integer hash)
atom angle
angle= 2 * PI * hash / 256.0
return {cos(angle), sin(angle)}
end function
-- Linear interpolation function
function lerp(atom a, atom b, atom t)
return a + t * (b - a)
end function
-- Fade function to smooth out the interpolation
function fade(atom t)
return t * t * t * (t * (t * 6 - 15) + 10)
end function
-- Dot product of the gradient vector and the distance vector
function dot_grid_gradient(integer ix, integer iy, atom x, atom y)
atom dx, dy
sequence g
integer hash
-- Use permutation table to get a gradient hash
hash= permutation[mod(permutation[mod(ix, 256)] + iy, 256)]
g = gradient(hash)
-- Calculate the distance from the grid point
dx = x - ix
dy = y - iy
-- Return the dot product of the gradient and distance vectors
return dx * g[1] + dy * g[2]
end function
-- Main 2D Perlin noise function
global function perlin(atom x, atom y)
integer x0, x1, y0, y1
atom sx, sy, n0, n1, ix0, ix1
-- Determine grid cell coordinates
x0 = floor(x)
x1 = x0 + 1
y0 = floor(y)
y1 = y0 + 1
-- Calculate interpolation weights
sx = fade(x - x0)
sy = fade(y - y0)
-- Calculate noise contributions from the four corners
n0 = dot_grid_gradient(x0, y0, x, y)
n1 = dot_grid_gradient(x1, y0, x, y)
ix0 = lerp(n0, n1, sx)
n0 = dot_grid_gradient(x0, y1, x, y)
n1 = dot_grid_gradient(x1, y1, x, y)
ix1 = lerp(n0, n1, sx)
-- Interpolate the final value
return lerp(ix0, ix1, sy)
end function
-- Example usage: generating noise for a 10x10 grid
constant size = 10
for y = 0 to size - 1 do
for x = 0 to size - 1 do
printf(1, "%.2f ", {perlin(x * 0.1, y * 0.1)})
end for
puts(1, "\n")
end for